Student Loans: What You Need to Know Before Borrowing
Student loans can be a vital tool for funding your education, but understanding the details before borrowing is crucial to avoid financial pitfalls later on. Whether you’re a high school graduate heading to college or a graduate student pursuing advanced degrees, here’s what you need to know.
Types of Student Loans
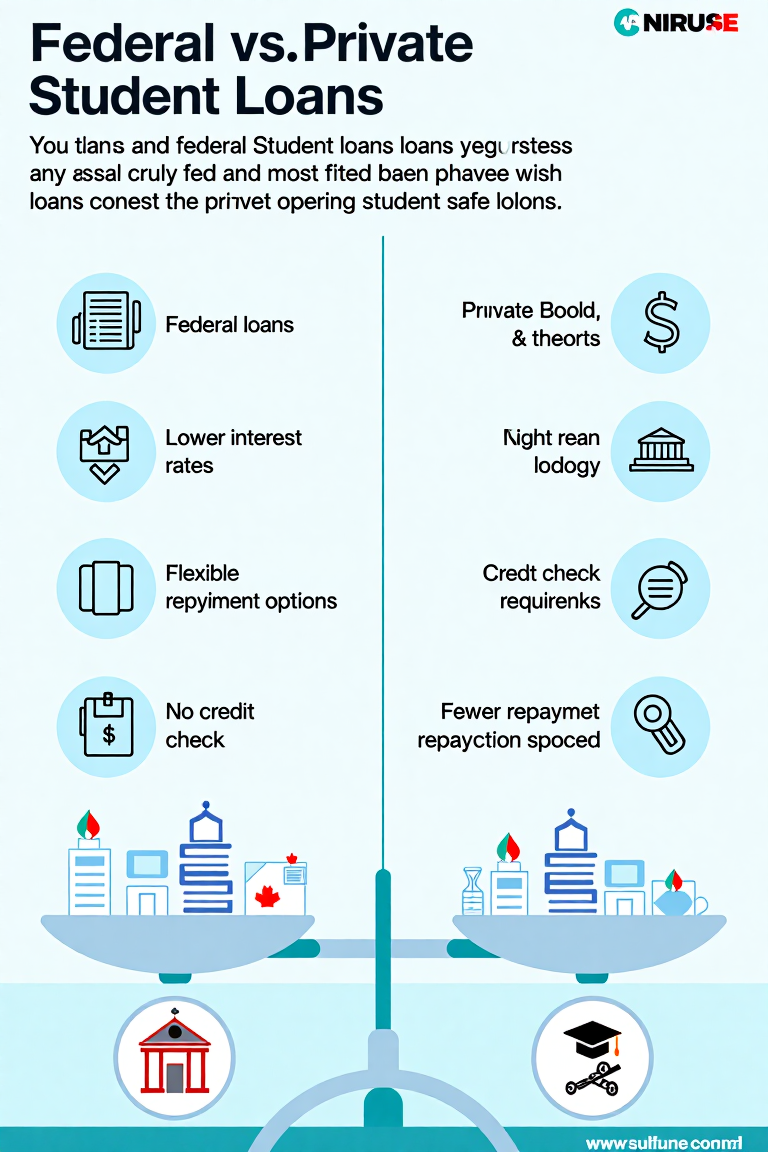
There are two main types of student loans: federal loans and private loans. Understanding the differences between them is essential for making the right choice.
- Federal Student Loans: These are loans provided by the U.S. Department of Education. They usually offer lower interest rates and more flexible repayment options compared to private loans. There are several types of federal loans, including Direct Subsidized Loans, Direct Unsubsidized Loans, and PLUS Loans for parents and graduate students.
- Private Student Loans: These loans are offered by banks, credit unions, or other financial institutions. Private loans typically have higher interest rates and fewer repayment options than federal loans. Your credit score and the creditworthiness of your cosigner can significantly affect the terms of the loan.
Interest Rates and Repayment Terms
Interest rates for student loans vary depending on the type of loan and whether it is federal or private. Federal loans have fixed interest rates set by Congress, whereas private loan rates can be fixed or variable, and are determined by the lender based on your credit score.
Repayment terms also vary. For federal loans, there are multiple repayment plans, including income-driven options that adjust based on your income. Private loans may offer more limited options for repayment and might require you to start paying while you’re still in school, depending on the lender.
How to Borrow Responsibly
- Only Borrow What You Need: Student loans can quickly accumulate, and borrowing more than you need can leave you with a heavy debt burden. Only borrow the amount that is necessary to cover your tuition and living expenses.
- Understand the Total Cost: Before borrowing, understand how much you’ll need to repay after you graduate. Student loan calculators can help you estimate your monthly payments and total repayment cost.
- Consider Future Earnings: Take into account your career goals and expected income. Borrowing too much can become a strain on your finances later, especially if your chosen career path doesn’t have a high earning potential.
- Look for Scholarships and Grants First: Before turning to loans, explore scholarships, grants, and work-study opportunities that don’t need to be repaid.
The Importance of Credit Scores
Your credit score is important when applying for private student loans, as it will influence the interest rate and loan terms. Federal loans do not require a credit check, but private loans typically do. A higher credit score can help you secure more favorable loan conditions, while a lower score may lead to higher interest rates.
Loan Forgiveness and Repayment Assistance
Some federal student loans offer loan forgiveness programs, especially for those working in public service jobs or teaching in underserved areas. Explore all repayment options, including income-driven plans, to see if you qualify for assistance.




