Hedge Funds vs. Mutual Funds: Key Differences and Which Is Right for You
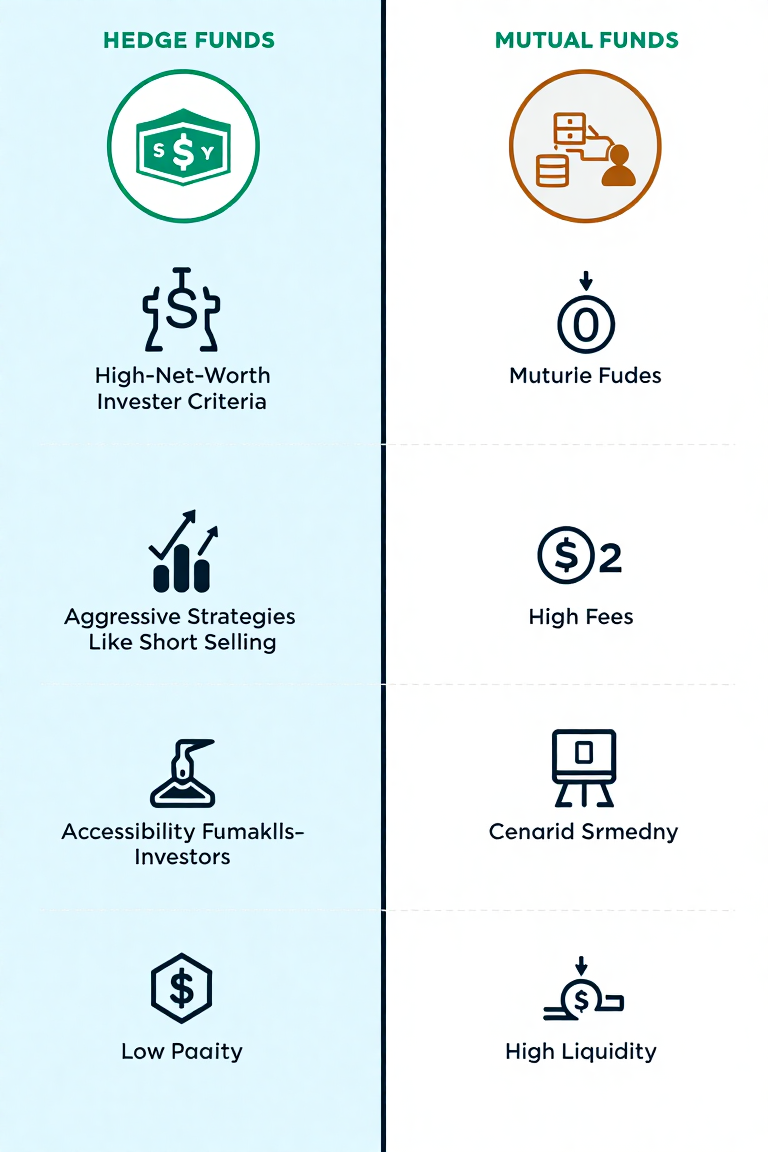
When deciding how to invest your money, understanding the differences between hedge funds and mutual funds is crucial. Both options offer professional management and portfolio diversification, but they differ significantly in terms of accessibility, strategy, risk, and potential returns. Here’s a detailed comparison to help you choose the best option for your financial goals.
1. Accessibility
- Hedge Funds:
Hedge funds are typically reserved for accredited investors—individuals or institutions that meet specific income or net worth criteria. This exclusivity makes them inaccessible to the average investor.- Example Criteria: A net worth of $1 million (excluding primary residence) or an annual income exceeding $200,000 for the past two years.
- Mutual Funds:
Mutual funds are open to all investors, with no wealth or income requirements. They often have low minimum investment thresholds, making them an excellent option for beginners.
2. Investment Strategies
- Hedge Funds:
Hedge funds employ aggressive and diverse strategies, such as short selling, leverage, and derivatives. They aim for high returns, often targeting niche opportunities or exploiting market inefficiencies.- Common Strategies: Long-short equity, global macro, event-driven, and arbitrage.
- Mutual Funds:
Mutual funds take a more conservative approach, focusing on long-term growth and capital preservation. They invest primarily in stocks, bonds, or a mix of both, depending on the fund’s objective.- Example Types: Equity funds, bond funds, index funds, and balanced funds.
3. Risk and Regulation
- Hedge Funds:
Hedge funds operate with fewer regulatory constraints, allowing them to pursue riskier strategies. However, this freedom comes with a higher level of risk and the potential for significant losses. - Mutual Funds:
Mutual funds are heavily regulated, with strict rules to protect investors. These regulations limit the fund manager’s ability to use high-risk strategies, making mutual funds a safer choice.
4. Liquidity
- Hedge Funds:
Hedge funds are less liquid, often requiring investors to lock in their money for a set period (e.g., months or years). Withdrawals may only be allowed at specific intervals. - Mutual Funds:
Mutual funds offer daily liquidity, allowing investors to buy or sell shares at the fund’s net asset value (NAV) at the end of each trading day.
5. Fees
- Hedge Funds:
Hedge funds typically follow a “2 and 20” fee structure:- Management Fee: 2% of the fund’s total assets annually.
- Performance Fee: 20% of the profits above a specified benchmark.
- Mutual Funds:
Mutual funds charge lower fees, usually expressed as an annual expense ratio (0.5% to 1.5%). Index funds, a type of mutual fund, often have fees below 0.1%.
6. Return Potential
- Hedge Funds:
Hedge funds aim for high absolute returns, often outperforming traditional markets during favorable conditions. However, their performance can be volatile and inconsistent. - Mutual Funds:
Mutual funds generally aim for relative returns, striving to match or exceed a benchmark index. While returns may be lower than hedge funds, they are often more stable.
Which Is Right for You?
- Hedge Funds:
Suitable for high-net-worth individuals seeking aggressive growth and willing to accept higher risk and lower liquidity. Hedge funds can complement an already well-diversified portfolio. - Mutual Funds:
Ideal for average investors looking for accessible, diversified, and low-risk investment options. Mutual funds are well-suited for long-term financial goals like retirement or education savings.
Conclusion
Choosing between hedge funds and mutual funds depends on your financial situation, risk tolerance, and investment goals. Hedge funds offer high-risk, high-reward opportunities, while mutual funds provide a safer, more accessible path to wealth building. Evaluate your needs carefully to make the right choice.




